memcpy
- 完成内存的拷贝
- 如果内存有重叠(对小端),则从高位到低位复制
- 如果内存无重叠,则从低位到高位传递
void* my_memcpy(void *dst, void *src, size_t count){
if(dst == nullptr || src == nullptr){
return nullptr;
}
char* temp_dst = (char*) dst;
char* temp_src = (char*) src;
if(temp_dst > temp_src && temp_dst < temp_src+ count){
// 内存重叠
temp_dst = temp_dst + count -1;
temp_src = temp_src + count -1;
while(count--){
*temp_dst-- = *temp_src--;
}
}
else {
while(count--){
*temp_dst++ = *temp_src++;
}
}
return (void * )dst;
}
排序算法
排序算法比较

插入排序
直接插入排序:复杂度O(n^2)

原理
- 将无序元素一个一个插入到有序部分中
- 对于待排序元素
temp = index.1:length-1,寻找其左侧有序序列index.0:temp-1的插入位置 - 对index从 temp-1 到 0 过程中
- temp > index值
- a[index+1] = temp
- temp < index值(如果没有到头部)
- 在下一次处理(a[index+1] = a[index])
- temp < index值(在头部)
- 本次处理 a[index] = temp;
- temp > index值
- 对于待排序元素
伪码
// 待排序数组
for(index_1 := 1:length-1):
// 将待排序元素取出
temp = a[index_1]
// 排序位置index
for(index_2 := index_1:0):
// for循环执行之后的下一次处理
a[index_2+1] = a[index_2];
// 如果可以放入
if(temp > a[index_2]){
a[index_2 + 1] = temp;
}
// 对于头部的处理
if(temp < a[index_2] && index_2 ==0){
a[index_2] = temp;
}
代码
void straight_inserting_sort(int a[], int length){
// 对所有待排序元素来说
for(int i = 1; i <length; i++){
// 如果比排好序的序列的最大值小
if(a[i] < a[i-1]){
int temp = a[i];
// 从序列最大值遍历排好序的序列[0,i-1]
for(int j = i - 1; j >=0 ; j--){
a[j + 1] = a[j];
// 如果找到该位置
if(a[j] < temp){
a[j+1] = temp;
break;
}
// 如果该值最小
if(a[j] > temp && j == 0 ){
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
折半插入排序

- 将右侧数组的元素逐个插入到左侧排好序的数组
- 确定排好序数组的ordered_index := 0:index-1
- 利用二分搜索查找插入点index+1 >temp
- 将index右侧所有值均右移一位
- 将值赋值到index+1位置
伪码
for(index := 1:length-1){
temp = a[index];
left = 0, right = index -1
while(left <= right){
mid = left + (right-left) /2;
if(a[mid] > temp){
right = mid-1
}
else{
left = mid+1;
}
}
for(right右侧){
全部右移一位
}
值赋值
}
void binary_insert_sout(int a[], int length){
int low, high, mid;
for(int i = 1 ; i <length ; i++){
low = 0;
high = i - 1;
temp = a[i];
while(high >=low){
mid = low+ (high - low) /2;
if(temp < a[mid]){
high = mid -1;
}
else {
low = mid +1;
}
}
// 选择high而不是low的原因:
for(int j =i - 1 ; j > high ; j--){
a[j+1] = a[j];
}
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
冒泡排序:O(n^2)

- 冒泡排序每次都会将最大值放在数组末尾
void bubble_sort(int a[], int length){
for(int i = 0; i <length -1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < length - i-1; j++){
if(a[j] >a[j+1]){
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j]+1 = temp;
}
}
}
}
选择排序:O(n^2)

void select_sort(int a[], int length){
for(int i = 0; i <length-1; i++){
int min_index = i;
for(int j = i+1; j <length; j++){
if(a[min_index] >a[j]){
min_index = j;
}
}
if(i != min_index){
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[min_index];
a[min_index] = temp;
}
}
}
希尔排序:O(nlogn)

void shell_sort(int a[], int length){
int i, j, gap;
for(gap = length/2; gap >0; gap /=2){
for(i = 0; i < gap; i++){
for(j = i + gap; j < length; j += gap){
int temp = a[j];
k = j - gap;
while(k >=0 && a[k] > temp){
a[k + gap] = a[k];
k -= gap;
}
a[k + gap] = temp;
}
}
}
}
快速排序:O(nlogn)
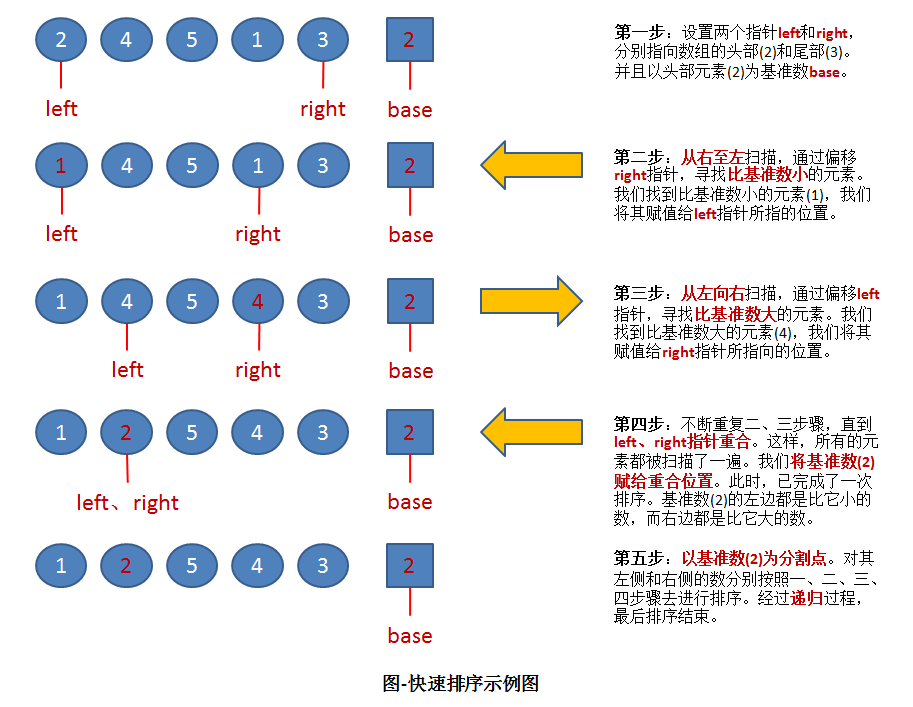
void quick_sort(int[] a, int low, int high){
if(low < high){
int key = quick_sort_index(a, low, high);
quick_sort(a, low, key-1);
quick_sort(a, key+1, high);
}
}
int quick_sort_index(int[] a, int low, int high){
int temp = a[low];
int rightvalue;
int leftvalue;
while(low < high){
while(low < high && a[high] >= temp){
high--;
}
a[low] = a[high];
while(low < high && a[low] <=temp){
low++;
}
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = temp;
return low;
}
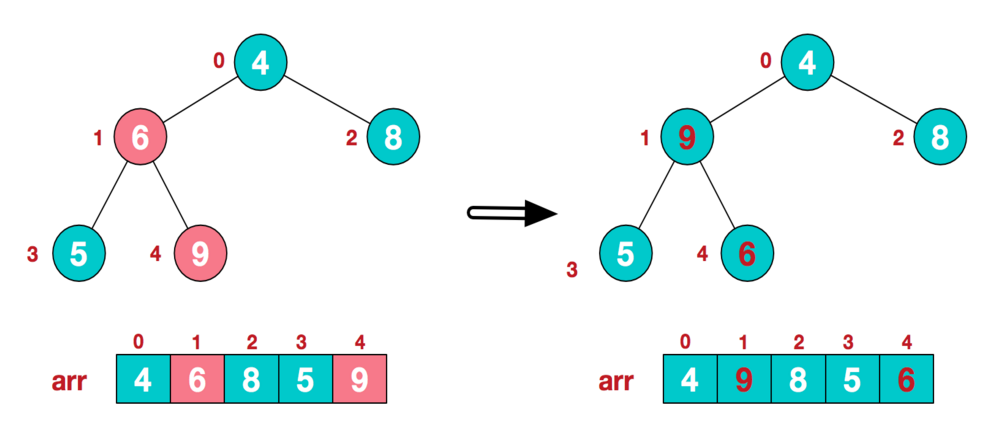
堆排序:O(nlogn)
步骤
- 无序序列建立完全二叉树
- 从最后一个叶子节点开始,从左到右,从下到上调整,将完全二叉树调整为大根堆
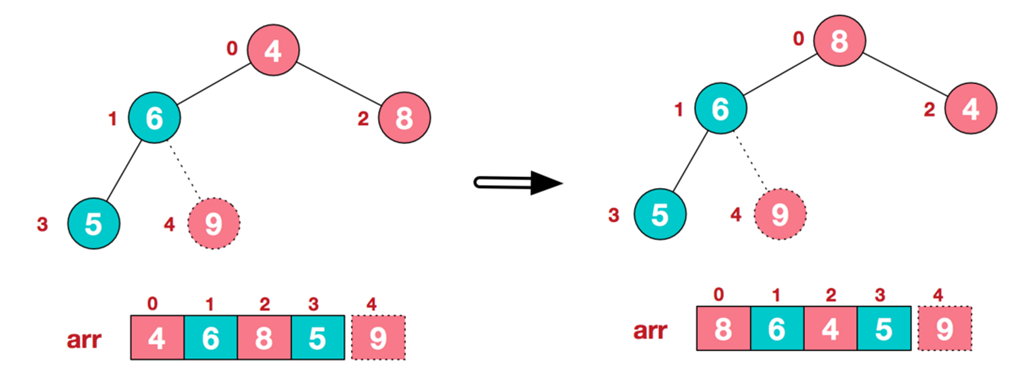
- 找到第1个非叶子节点6,由于6的右子节点9比6大,所以交换6和9。交换后,符合大根堆的结构
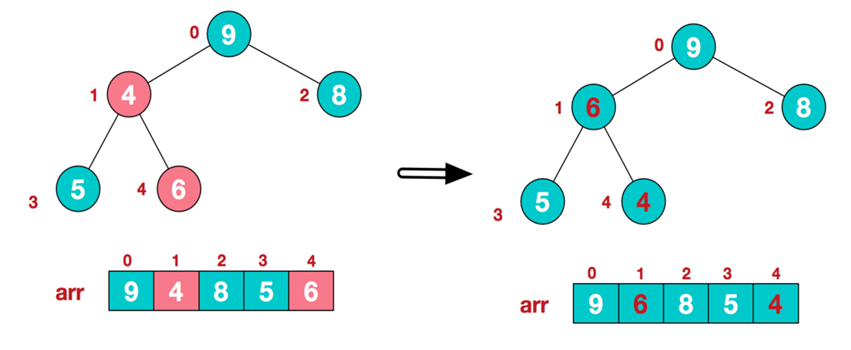
- 找到第2个非叶子节点4,由于的4左子节点9比4大,所以交换4和9。交换后不符合大根堆的结构,继续从右到左,从下到上调整。
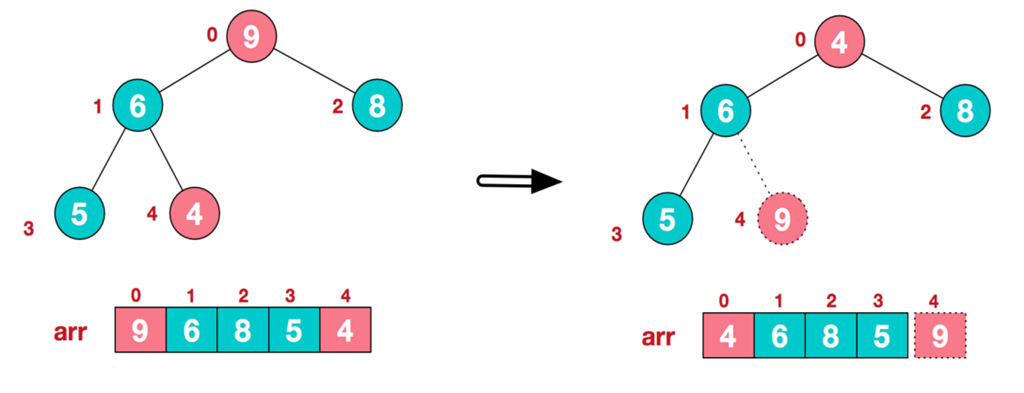
- 交换堆元素(交换堆首和堆尾元素–获得最大元素)
- 重建大根堆(前n-1个元素)
- 重复执行步骤二和步骤三,直到整个序列有序 图



void heap_sort(vector<int>& arr, int length){
for(int i = length/2 -1; i>=0 ; i++){
adjust(arr, length, i);
}
for(int i = size -1; i>=0 ; i--){
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
adjust(arr, i, 0);
}
}
void adjust(vector<int>& arr, int length, int index){
int left = 2*index + 1;
int right = 2*index +2;
int maxindex = index;
if(left < length && arr[left] > arr[maxindex]) maxindex = left;
if(right< length && arr[right] > arr[maxindex]) maxindex = right;
if(maxindex != index){
swap(arr[maxindex], arr[index]);
adjust(arr, length, maxindex);
}
}
void swap (int value1, int value2){
int temp = value1;
value1 = value2;
value2 = temp;
}
归并排序:O(nlogn)

void merge_sort(int[] a, int low, int high){
if(low < high){
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
merge_sort(a, low, mid);
merge_sort(a, mid+1, high);
merge(a, low, mid, high);
}
void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high){
int i = low;
int j = mid +1;
k = 0;
int* temp = new[high - low - 1];
while(i <=mid && j <= high){
if(a[i] <= a[j]){
temp[k++] = a[i++];
}
else {
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){
temp[k++] = a[i++];
}
while(j <= high){
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
for(i = low, k = 0; i<= high; i++,k++){
a[i] = temp[i];
}
delete[] temp;
}
}
计数排序O(n+k)

void count_sort(int[] a, int length){
int max = a[0];
int i = 0;
while( i< length -1){
max = (a[i] > a[i+1]) ? a[i]: a[i+1];
i++;
}
int* countArray = new int[max+1]{0};
int* temp = new int[length];
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
countArray[a[i]]++;
}
// 特别注意此方法实现,可以减少复杂度
for(int i = 1; i < length + 1; i++){
countArray[i] += countArray[i-1];
}
// 反向遍历
for(int i = length-1; i >= 0 ; i--){
temp[countArray[a[i]]-1] = a[i];
countArray[a[i]]--;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < length; i++){
a[i] = temp[i];
}
delete[] countArray;
delete[] temp;
}
基数排序O(n*k)

int get_max_digits(int[] a, int length){
int max = a[0];
int i = 0;
while(i < length-1){
max = (a[i] > a[i+1]) ? a[i]: a[i+1];
}
int b =0;
while(max > 0){
b++;
max /= 10;
}
return b;
}
void sort(int[] a, int length){
int d = get_max_digits(a, length);
int* temp = new int[length];
int padding = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < d; i++){
int count[10]={0};
for(int j = 0; j <length; j++){
int tail_number = (a[j]/padding) % 10;
count[tail_number]++;
}
for(j = 1; j <10; j++){
count[j] += count[j-1];
}
for(int j = length-1; j >=0; j--){
int tail_number = (a[j] / padding) % 10;
temp[count[tail_number] - 1] = a[j];
count[tail_number]--;
}
for(int j = 0; j < length;j++){
b[j] = temp[j];
}
radix *= 10;
}
delete[] temp;
}
桶排序:O(n+k)

void bucket_sort(int[] a, int length){
int max = INT_MIN;
int min = INT_MAX;
for(int i = 0; i <length; i++){
if(a[i] > max) max = a[i];
if(a[i] < min) min = a[i];
}
int bucket_len = max - min +1;
int bucket[bucket_len];
for(int i = 0; i < bucket_len; i++){
bucket[i] = 0;
}
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < length ; i++){
index = arr[i] - min;
bucket[index]++;
}
int start = 0;
for(int i = 0; i< bucket_len; i++){
for(int j = start; j < start + bucket[i]; j++){
a[j] = min + i;
}
start += bucket[i];
}
}